Blog Post
The RefererNotAllowedMapError is a common error that might arise when you attempt to utilize various Google Maps APIs, such as the Google Maps JavaScript API or the Google Maps Geocoding API. This error essentially points out that the particular website or domain initiating the API request isn’t included in the list of authorized referrers for the specific API key being employed. This error acts as a sort of gatekeeper, ensuring that only pre-approved sources can access the requested services through the API key.
Causes of RefererNotAllowedMaperror

If you see this google maps error in the javascript console: “google maps javascript api error: referernotallowedmaperror”, this RefererNotAllowedMapError can be attributed to a few key reasons:
- Incorrect API Key Association: The API key in use might not be correctly associated with the appropriate project. To leverage a Google Maps API, the API key must be linked to a project that possesses the necessary permissions and access for utilizing the specific API.
- Unauthorized Referrers: When making an API request, it’s vital to specify the list of permitted websites or domains that can utilize the API key. If the requesting website or domain isn’t included in this list of allowed referrers, the RefererNotAllowedMapError will be triggered as a security measure.
- API Key Issues: In cases where the API key lacks the essential permissions or is invalid, the RefererNotAllowedMapError may be encountered. It’s crucial to ensure that the API key is properly configured with the required authorizations to utilize the desired API functionality.
Steps to fix the RefererNotAllowedMapError
- Click the project drop-down menu at the top of the page, and select the project that you want to modify the authorized referrers.
- Click the hamburger menu and select APIs & Services > Credentials.
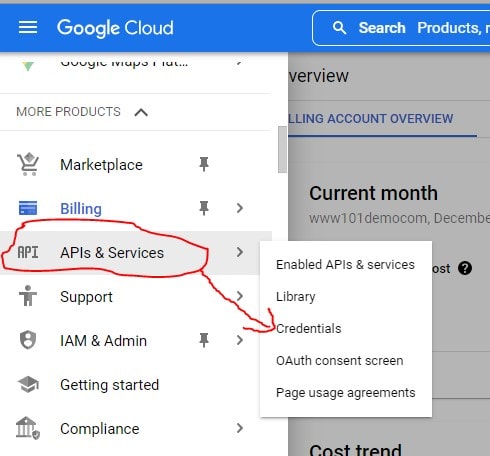
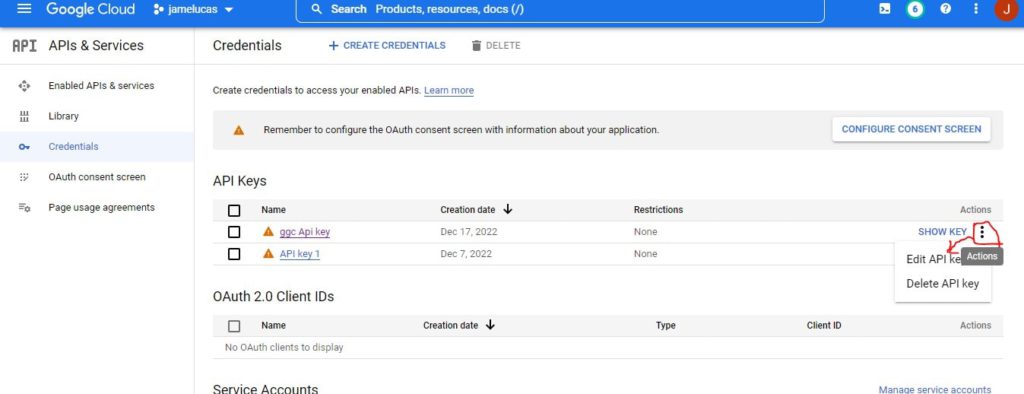
- Click the name of the API key that you want to modify.
- Click the Edit button in the restriction section > In the Key Restrictions section, select the Websites referrers option.
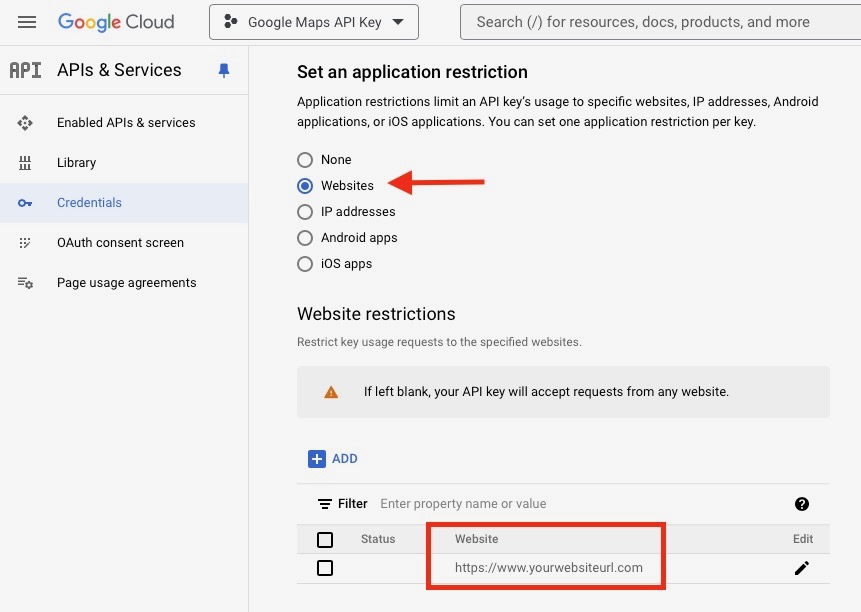
- In the Add Website field, enter the list of allowed websites for the API key. Follow the instructions below to correctly set up your website URL.
- Single Domain URL: For single domain website, use one of the below website url as per your website domain.
- Use https://example.com for without www url and ssl is enabled.
- Use https://www.example.com – for url with www and ssl is enabled.
- Use http://www.example.com for url with www and ssl is not enabled.
- use http://example.com for without www url and ssl is not enabled.
- Single Subdomain URL: If you’re showing your google maps in a sub-domain.
- Use https://sub.example.com if ssl is enabled.
- Use http://sub.example.com if ssl is not enabled.
- All Subdomains in a Single Domain using a Wildcard: if you have multiple subdomains then you can use regular expression format.
- Use https://*.example.com if ssl is enabled.
- Use http://*.example.com if ssl is not enabled.
- Single Domain URL: For single domain website, use one of the below website url as per your website domain.
- Click the “Save” button to update the Key restrictions for the API key.
Conclusion
The RefererNotAllowedMapError arises from a specific cause: the referrer’s absence on the list of authorized referrers for the API key. To effectively address this error and restore proper functionality, consider the following steps:
- Review Application Restrictions: Ensure that the API key being used has appropriate application restrictions configured. Double-check that the domain of the referrer making the API request is explicitly listed within the allowed referrers.
- Use the Correct API Key: Verify that the correct API key is being utilized by the referrer. Confirm that the API key has the necessary permissions and is accurately associated with the intended project.
By implementing these measures, you can resolve the RefererNotAllowedMapError, ensuring seamless communication with the Google Maps API while maintaining security and access control.

Recent Posts
Loading recent posts...


